Signs of skin dehydration
Skin dehydration occurs when the skin lacks adequate moisture and water. Skin can appear dull, dry and less supple.
Common signs are rough texture, tightness and discomfort, flakiness and peeling, increased sensitivity, redness, decreased elasticity and also fine lines and wrinkles.
Claims related to hydration
Moisturizing
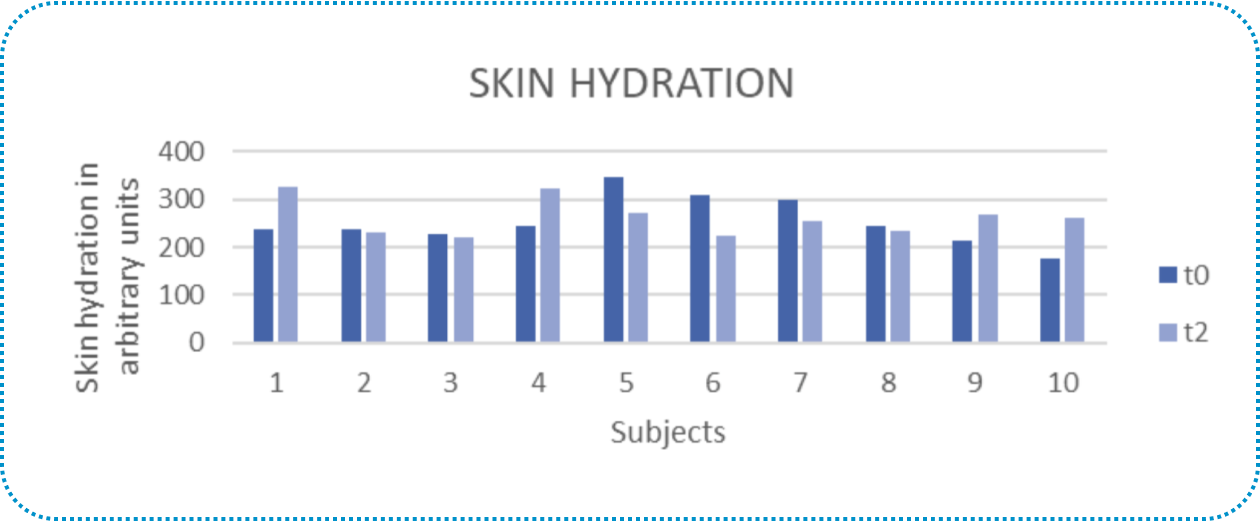
Hydrating