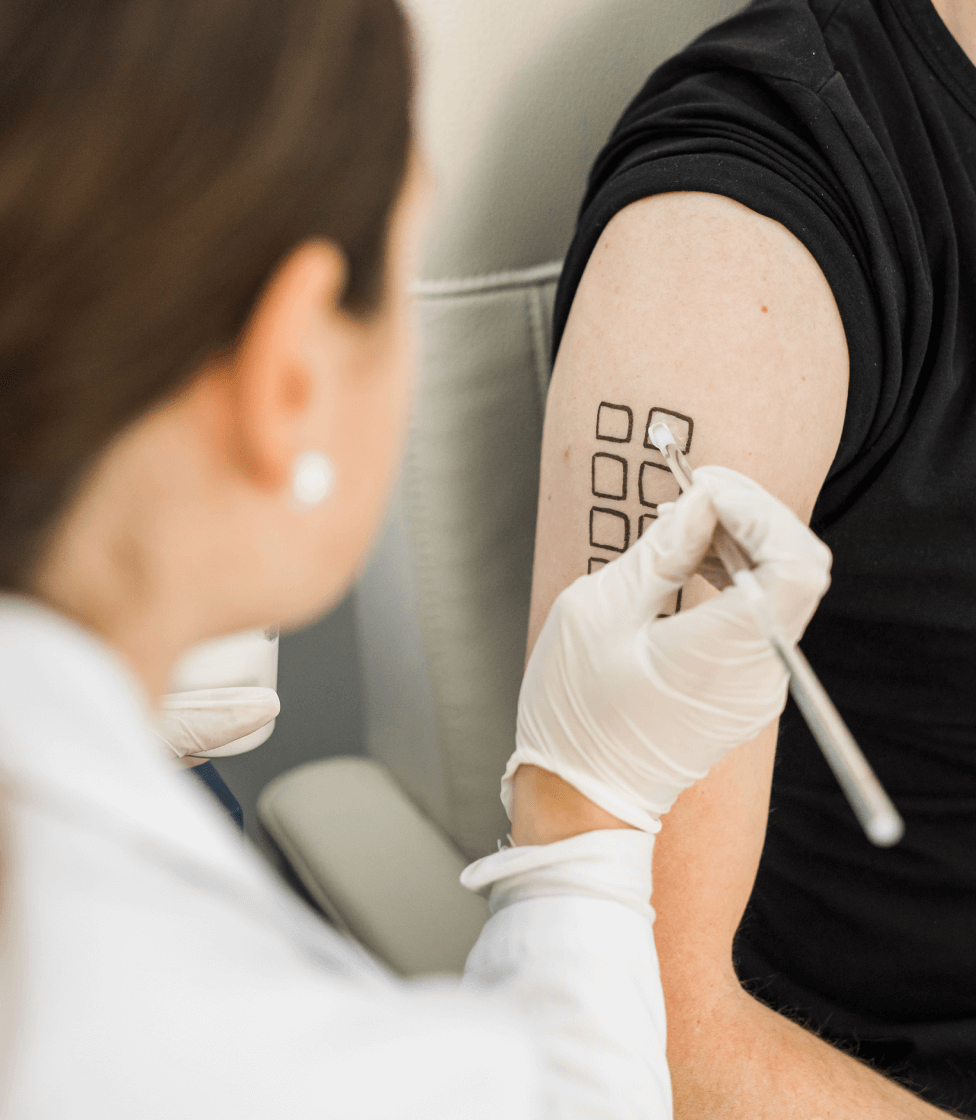How is a patch test performed?
Patch test is performed by applying approximately 0.2g or 0.2ml of the cosmetic product on the intact skin on the arm or on the back of adult subjects. The area where the product has been applied is then covered with an occlusive or semi-occlusive patch for 48 hours. Observations of the effects caused by the application of the product on the skin are performed 1 hour and 24 hours after the patch is removed. These observations are done under the supervision of a dermatologist, which then also enables the companies to claim that their products have been dermatologically tested.
Products are applied to the skin either in a pure state or diluted, depending on the type of product and on the intended use. Leave-on products are applied undiluted, while rinse-off products are diluted either in demineralized water or in mineral oil. Test products that contain high levels of, or ingredients that require dilution in, volatile solvents that are to be applied using occlusive patches may need to be left to evaporate for a couple of minutes before application to the skin.